NAT Instance (e.g. let’s call it- NATIN) is an EC2 instance running an AMI image that has NAT functionality configured.
NATIN maintains a table (called ATT or Address Translation Table) to map internal IPs and source (ephemeral) port number to an external IP address and port number.
This variation of NAT that uses port number to map multiple Internal IPs to one external IP is called PAT (Port Address Translation) or Single Address NAT.
An NAT Instance computer needs to reside in a Public Subnet and needs to be secured by its own Security Group (let’s call it: NATSG).
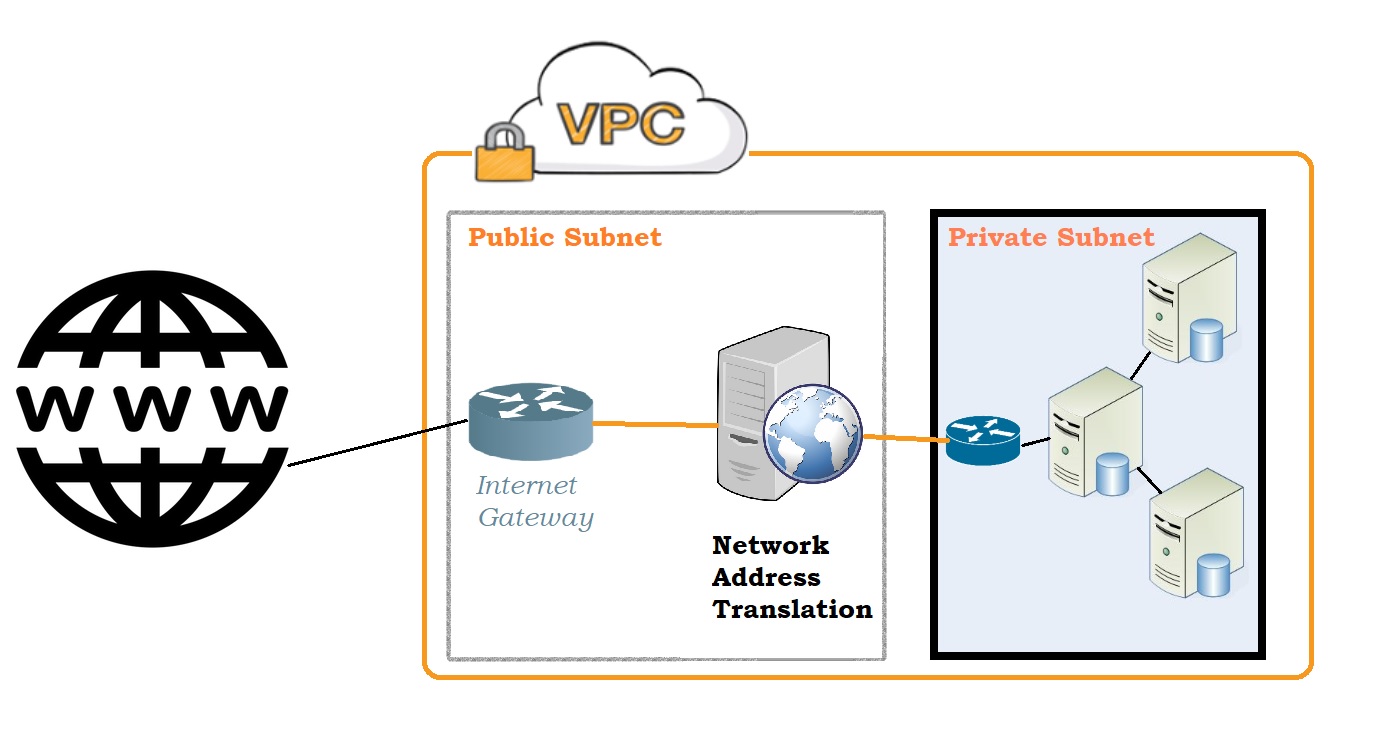
The NATSG should allows Incoming traffic from Private Subnet’s Security Group on acceptable protocols and ports.
NATSG should also allow Outgoing traffic to 0.0.0.0/0 on acceptable protocols and ports.
The EC2 instance that run NAT instance, should have the “Source Destination Check” disabled, since AWS rejects traffic on an EC2 instance where either the source or destination doesn’t match it’s own IP.
When an NAT Instance is created within a VPC and there are EC2 instances created, then the VPC cannot be deleted unless the NAT instance is deleted.
NAT Gateway (e.g. following the same terminology, let’s call it- NATGW) is an AWS managed service that provides functionality similar to the NAT instance.
NATGW do not require management efforts from users, since it is managed by AWS.
NATGW works only with an Elastic IP address (not Public IP address).
NATGW cannot be assigned a Security Group (since it is managed by AWS and it is not an Instance).
Often NATGW is a better choice to use than NATIN because there is less maintenance effort on users’ side and AWS does it’s maintenance, while offering high availability and better SLAs. It is also AWS recommended option.
NATGW is managed by AWS but it is provisioned by the Admin. NATGW must be created in public subnet.
The routing table associated with public subnet (containing NATGW) must include a route 0.0.0.0/0 that points to IGW.
The NACL associated with public subnet, must allow incoming/outgoing traffic from/to all private subnets that need Internet access.
Routing tables of private subnets must point to NATGW (in public Subnet) for all outgoing traffic designated to 0.0.0.0/0

Leave a comment